Water is a fundamental resource essential for human survival, industrial applications, and environmental sustainability. However, natural water sources often contain impurities that must be removed to ensure safety and usability. Water treatment is the process of purifying water by eliminating contaminants, making it suitable for drinking, industrial operations, and environmental conservation. This intricate process involves multiple stages, including filtration, chemical treatment, and advanced purification technologies.
Understanding Water Contaminants
Water can contain various contaminants that impact health and industrial processes. These impurities are classified into different categories:
Physical Contaminants: Sediments, suspended particles, and organic matter that can make water turbid.
Chemical Contaminants: Heavy metals (lead, mercury, arsenic), pesticides, chlorine, and industrial waste that pose serious health risks.
Biological Contaminants: Bacteria, viruses, protozoa, and algae that cause waterborne diseases.
Radiological Contaminants: Radioactive substances like uranium and radon that can be hazardous if consumed.
Key Stages of Water Treatment
To ensure water safety and quality, a combination of purification methods is used:
Coagulation and Flocculation: Chemicals like alum are added to water to bind with suspended particles, forming larger clumps (flocs) that can be easily removed.
Sedimentation: The heavy flocs settle at the bottom of the treatment tanks, separating from the clear water.
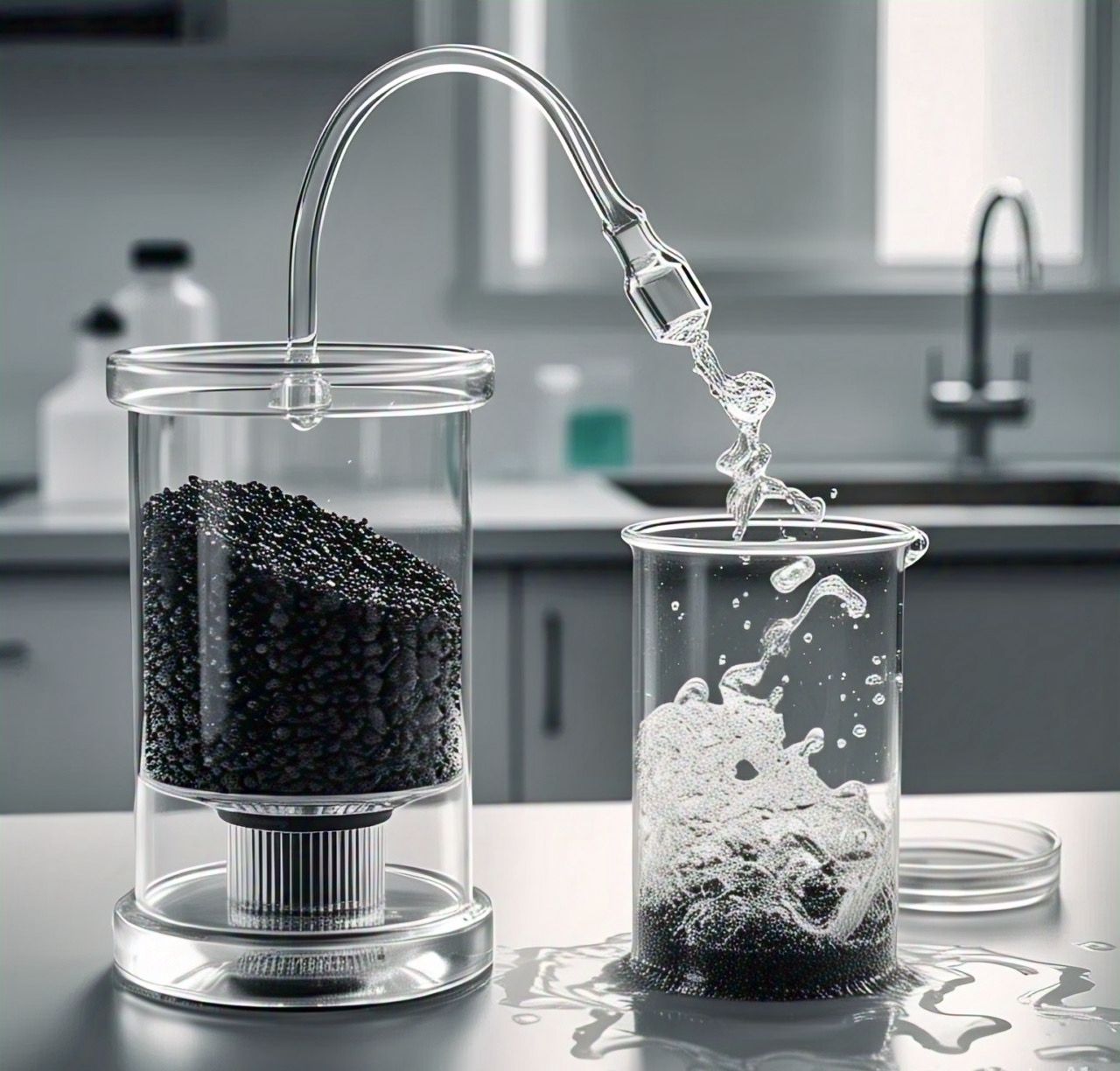
Filtration: Water passes through various filters (sand, gravel, activated carbon) to remove finer particles, bacteria, and organic compounds.
Chemical Disinfection: Chlorination, ozonation, or ultraviolet (UV) treatment is used to kill harmful microorganisms.
Advanced Purification Technologies:
Reverse Osmosis (RO): Uses semi-permeable membranes to remove dissolved salts, minerals, and impurities.
Activated Carbon Adsorption: Removes organic chemicals, chlorine, and odors by trapping contaminants in porous carbon.
Ion Exchange: Softens water by replacing harmful ions (calcium, magnesium) with sodium or potassium ions.
Applications of Water Treatment
Water treatment is critical in multiple sectors, ensuring safe consumption and operational efficiency:
Drinking Water Treatment: Municipal water treatment plants purify water to meet safety standards for public consumption.
Industrial Water Treatment: Factories and power plants require treated water for cooling systems, boilers, and manufacturing processes.
Wastewater Treatment: Removes pollutants from sewage and industrial discharge before releasing water back into the environment.
Agricultural Water Treatment: Ensures irrigation water is free from harmful contaminants that could affect crops and soil health.
Benefits of Effective Water Treatment
Investing in efficient water treatment systems offers numerous advantages:
Public Health Protection: Reduces the risk of waterborne diseases and chemical exposure.
Environmental Sustainability: Minimizes pollution and conserves water resources.
Industrial Efficiency: Prevents equipment corrosion, scaling, and contamination in industrial applications.
Economic Savings: Reduces medical costs, infrastructure damage, and operational inefficiencies.
Future Trends in Water Treatment
With growing concerns about water scarcity and pollution, the industry is evolving with innovative solutions:
Smart Water Treatment Technologies: IoT and AI-based monitoring systems optimize filtration efficiency and detect contaminants in real time.
Desalination Advancements: More energy-efficient desalination methods are being developed to convert seawater into fresh water.
Eco-Friendly Treatment Solutions: Research focuses on biodegradable chemicals and renewable energy-powered treatment plants.
Conclusion
Water treatment plays a vital role in safeguarding public health, supporting industries, and protecting the environment. As demand for clean water rises, adopting advanced purification techniques and sustainable solutions is crucial for a healthier future. By implementing effective water treatment practices, we can ensure a continuous supply of safe and clean water for generations to come.